티스토리 뷰
※ 이해와 학습을 위해 원본 코드의 추가/수정이 있을 수 있습니다.
※ 인프런 강의: 개복치개발자님의 [입문편] 안드로이드를 위한 코틀린(Kotlin) 문법의 학습 기반으로 작성했습니다.
※ InterviewBit Kotlin 설명을 참고합니다.
※ 정보의 공유 사회(https://ddolcat.tistory.com/) 설명 및 예제를 참고합니다.
※ Programize(http://learning.coreref.com/www.programiz.com/kotlin-programming) 설명 및 예제를 참고합니다.
※ Udemy The Complete Android 12 & Kotlin Development Masterclass 설명 및 예제를 참고합니다.
- Null 안정성을 위한 Safe call operator (?.)
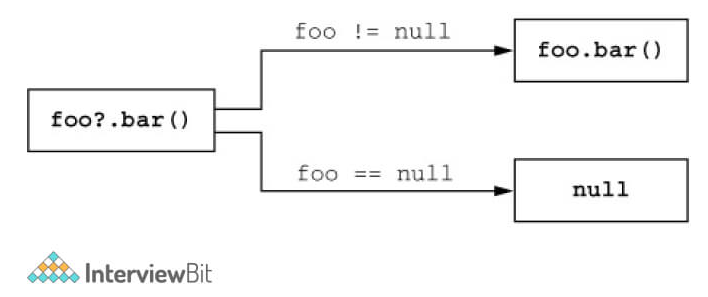
- 특정 변수값의 null을 허용할 때는 자료형+?
val test16: String? = null
val test16: String? = "abc"- null이 될 수 있는 변수의 값을 null이 될 수 없는 변수로 넣을 때의 처리 방법 - 변수명+!!
fun main() {
var test1 : String = "a"
var test2 : String = "b"
test1 = test2
println(test1)
// null이 될 수 있는 변수의 값을 null이 될 수 없는 변수에 넣을 때의 처리 방법
var test3 : String = "c"
var test4 : String? = "d"
test3 = test4!!
println(test3)
}
결과
==========================================
b
d- 엘비스 연산자
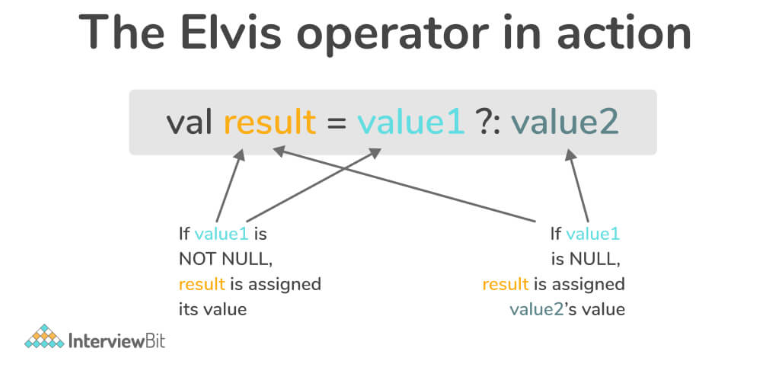
- 엘비스 연산자-#1
// 엘비스 연산자(Elvis Operator)
// null 처리를 위해
fun main() {
var testStr1 : String = ""
println(testStr1)
var testStr2 = null
println(testStr2)
var testStr3 : String = "abcd"
// var testStr4 : String = null
// 위 실행시 에러: Null can not be a value of a non-null type String
var testStr4 : String? = null
}
결과
==================
null- 엘비스 연산자-#2
fun main() {
println(findStringLength4("asdf"))
println(findStringLength4(null))
}
// 문자열의 길이를 반환, null인 경우도 변수로 받을 수 있도록
//fun findStringLength1(str : String?) : Int? {
// return str?.length
//}
//fun findStringLength3(str : String?) : Int {
// var resultCount = 0
// if(str != null){
// resultCount = str.length
// }
// return resultCount
//}
// 엘비스 연산자를 이용해 null이 아니면 글자수를 null이면 0을 반환
fun findStringLength4(str : String?) : Int {
return str?.length ?: 0
}
결과
=========================
4
0- Nullables
// source: The Complete Android 12 & Kotlin Development Masterclass
fun main(){
// NULLABLES/OPTIONALS in Kotlin
// Kotlin supports nullability as part of its type System.
// That means You have the ability to declare whether
// a variable can hold a null value or not.
// By supporting nullability in the type system,
// the compiler can detect
// possible NullPointerException errors at compile time
// and reduce the possibility of having them thrown at runtime.
var name: String = "Denis"
// name = null // Compilation Error
var nullableName: String? = "Denis"
nullableName = null // Works
// Here name cannot/must not be null
val len = name.length
val upper = name.toLowerCase()
// but the same methods won't work on nullable types
//val len2 = nullableName.length
// Compilation Error
// error message: Only safe (?.) or non-null asserted (!!.) calls are allowed on a nullable receiver of type String?
//val upper2 = nullableName.toLowerCase()
// Compilation Error
// error message: None of the following functions can be called with the arguments supplied:
// public inline fun Char.toLowerCase(): Char defined in kotlin.text public inline fun String.toLowerCase():
// String defined in kotlin.text
// So how can we solve this? We could do a null check before hand
val nullableName2: String? = "Denis"
if(nullableName2 != null) {
println("Hello, ${nullableName2.toLowerCase()}.")
println("Your name is ${nullableName2.length} characters long.")
} else {
println("Hello, Guest")
}
// This works but seems to be quite some work...
// So how about we shorten the syntax...
// Kotlin provides a Safe call operator, ?.
// It allows you to combine a null-check and
// a method call in a single expression.
nullableName2?.toLowerCase()
// This is the same as:
if(nullableName2 != null)
nullableName2.toLowerCase()
else
null
// You can use methods on a nullable variable like this
val nullableName3: String? = null
println(nullableName3?.toLowerCase()) // prints null
println(nullableName3?.length) // prints null
// You can perform a chain safe calls:
//val wifesAge: String? = user?.wife?.age
// Let'S say we don’t want to print anything if
// the variable is null?
// In order to perform an operation only if the
// variable is not null, we can use the safe call
// operator with let -
val nullableName4: String? = null
nullableName4?.let { println(it.lowercase()) }
nullableName4?.let { println(it.length) }
// Prints nothing because there nullableName is null
// and we used let to prevent anything from being performed
// What if we would like to enter a default value?
// Then we can use the elvis operator ?:
val name2 = nullableName4 ?: "Guest"
//val wifesAge2: String? = user?.wife?.age ?: 0
// Not null assertion : !! Operator
// The !! operator converts a nullable type to a
// non-null type, and throws a NullPointerException
// if the nullable type holds a null value.
// This is risky, and you should only use it if
// you are 100% certain, that there will be a value in
// the variable.
val nullableName5: String? = null
nullableName5!!.lowercase() // Results in NullPointerException
}
결과
=========================
Hello, denis.
Your name is 5 characters long.
null
null
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at FileKt.main (File.kt:101)
at FileKt.main (File.kt:-1)
at jdk.internal.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0 (:-2)'Kotlin' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Kotlin 공부 - 조건문 if, when (0) | 2022.04.13 |
|---|---|
| Kotlin 공부 - 반복문 for, while (0) | 2022.04.13 |
| Kotlin 공부 - 함수, 람다, 고차 함수, infix 함수, scope함수 (0) | 2022.04.13 |
| Kotlin 공부 - Collections : List, Map, Set, Iterator, 정렬 (0) | 2022.04.13 |
| Kotlin 공부 - Class, Overloading, Inheritance, Abstract, Object, enum (0) | 2022.04.13 |
댓글
